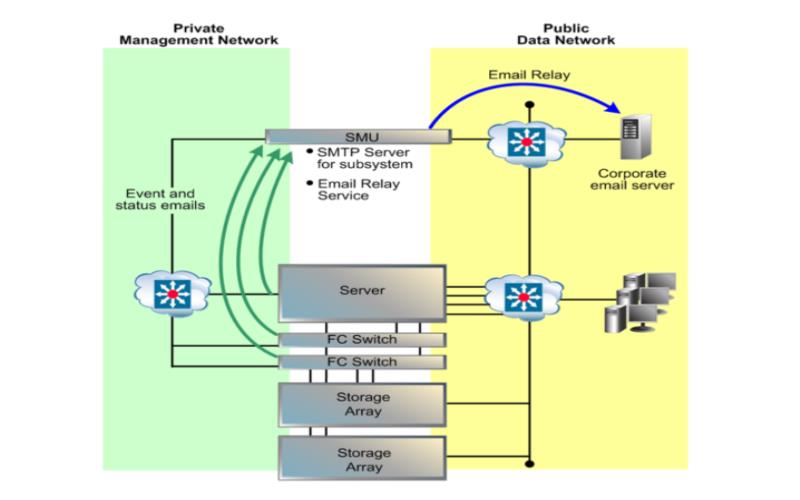
SMTP encryption, often referred to as Secure SMTP or SMTPS (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Secure), is a security mechanism used to protect the confidentiality and integrity of email messages as they are transmitted between email clients and SMTP servers. SMTP is the protocol Hostuserver responsible for the transfer of outgoing email messages from a sender’s email client to the recipient’s email server or mailbox. SMTP encryption ensures that email communication remains private and is safeguarded against eavesdropping or tampering during transit.
There are two primary methods of SMTP encryption:
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer):
SSL is a cryptographic protocol used to secure data transmission over the internet. When SSL is applied to SMTP, it is often referred to as SMTP over SSL (SMTPS). SMTPS encrypts the data exchanged between the email client and the SMTP server, ensuring that the email content and login credentials are protected from interception.
TLS (Transport Layer Security):
TLS is an updated and more secure version of SSL. When SMTP is configured to use TLS, it is referred to as SMTP over TLS or SMTP STARTTLS (an extension of the SMTP protocol). TLS encryption is initiated during the email transmission process, providing an additional layer of security.
Here’s how SMTP encryption works:
When an email client (sender) connects to an SMTP server (sender’s or recipient’s server) to send an email, the client and server perform a negotiation to determine if encryption is supported.
If both the client and server support encryption (SSL or TLS), they establish an encrypted communication channel.
All data, including the email message content, login credentials (if required for authentication), and any other communication between the client and server, is encrypted before transmission.
The encrypted data is decrypted by the receiving SMTP server, ensuring that the email message is delivered securely.
Benefits of SMTP Encryption:
Privacy: SMTP encryption protects the content of email messages from being intercepted or read by unauthorized parties while in transit.
Security: It safeguards login credentials used for SMTP authentication, preventing unauthorized access to email accounts.
Data Integrity: SMTP encryption ensures that email content remains unaltered during transmission, preventing tampering or modification by malicious actors.
Compliance: Many email regulations and standards, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), require the use of encryption to protect sensitive email communications.
Trust: Encrypted email transmission builds trust among email users, as they know their messages are secure during transit.
Email clients and SMTP servers are typically configured to support encryption, and users can enable encryption settings when setting up their email accounts. The choice of using SSL or TLS depends on the email provider and server configuration. It’s essential to configure email clients and servers correctly to ensure the encryption of email communication and enhance email security.
The benefits/advantages of SMTP Encryption
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) encryption, whether through SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security), offers several benefits and advantages that enhance finding out SMTP protocols the security and privacy of email communication. Here are the key benefits of SMTP encryption:
Confidentiality: SMTP encryption ensures that the content of email messages remains confidential during transmission. Encrypted emails are protected from eavesdropping and unauthorized access by third parties. This is particularly crucial for sensitive or confidential information.
Protection Against Eavesdropping: Without encryption, email messages can be intercepted and read by malicious actors or hackers while in transit over the internet. SMTP encryption prevents eavesdropping by encrypting the data exchanged between the email client and the SMTP server.
Secure Authentication: SMTP encryption safeguards login credentials (username and password) used for SMTP authentication. This prevents unauthorized access to email accounts, as the credentials are transmitted securely.
Data Integrity: Encryption helps maintain the integrity of email messages. It ensures that email content remains unaltered during transmission, preventing tampering or modification by attackers.
Compliance: SMTP encryption is often required to comply with data protection and privacy regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Compliance with these regulations is essential for businesses, healthcare providers, and organizations that handle sensitive data.
Enhanced Trust: Encrypted email transmission builds trust among email users. Knowing that their email communication is secure and private can lead to improved trust in the email service and sender.
Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: SMTP encryption helps defend against man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, where an attacker intercepts and potentially alters the communication between the email client and server. Encrypted communication makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to manipulate email content.
Secure Webmail Access: SMTP encryption is commonly used with web-based email services (webmail) to ensure secure communication between the user’s web browser and the email server. This protects email content and login credentials when accessing email through a web interface.
Global Accessibility: Encrypted SMTP communication can be safely used over public Wi-Fi networks or untrusted internet connections, reducing the risk of data interception in public settings.
Protection for Attachments: SMTP encryption extends protection to email attachments, ensuring that files attached to emails are transmitted securely.
Authentication of Email Servers: SMTP over TLS (STARTTLS) provides a means for email servers to authenticate each other, helping to confirm the legitimacy of the SMTP server receiving the message.
Reduced Spam and Phishing Risk: Encrypted SMTP communication makes it more challenging for spammers and phishers to intercept email traffic and launch attacks on email content or login credentials.
Overall, SMTP encryption is a fundamental security measure that safeguards the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of email communication. Implementing SMTP encryption is essential for individuals, businesses, and organizations to protect sensitive information, comply with regulations, and maintain trust in email communication.