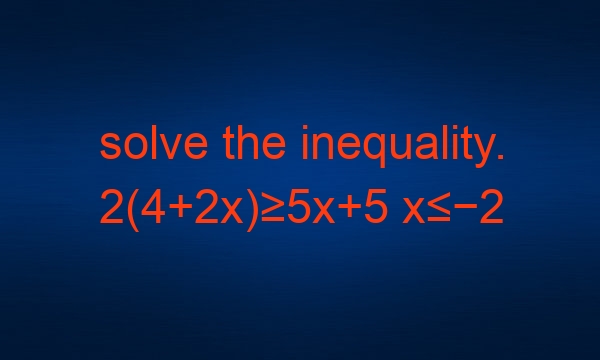The inequality 2(4+2x)≥5x+5 is a simple algebraic problem, but it can be tricky to solve. In this article, we’ll walk through the steps needed to solve the problem and discuss the different solutions for x.
Solving the Inequality
Solving the inequality starts by manipulating the equation to get an equation in terms of x. To do this, we need to isolate the x-term on one side of the equation. To do this, we start by subtracting 5 from both sides of the equation, resulting in: 2(4+2x) – 5 ≥ 5x.
Next, we divide both sides of the equation by 10. This results in: 2(4+2x)/10 ≥ 5x/10. Finally, we can factor out the 2x term, resulting in: 2x + 4 ≥ 5x/10.
Now that we have an equation in terms of x, we can solve for x. To do this, we subtract 4 from both sides of the equation, resulting in: 2x ≥ 5x/10 – 4. We can then divide both sides of the equation by 3x, resulting in: 2/3 ≥ 5/30 – 4/3x.
Finally, we can solve for x by multiplying both sides of the equation by 3x, resulting in: x≤−2.
Solutions for x
From the above equation, we can determine that the solution for x is x≤−2. This means that any value of x that is less than or equal to -2 will satisfy the inequality.
However, there are also other solutions for x. For example, if we multiply both sides of the original equation by -1, we can get the equation: -2(4+2x) ≤ 5x+5. We can then manipulate this equation in the same way as the original equation to get the equation: x≤3. This means that any value of x that is less than or equal to 3 will also satisfy the inequality.
Similarly, if we multiply both sides of the original equation by -1 and then divide both sides of the equation by -1, we can get the equation: 2(4+2x) ≥ -5x-5. We can then manipulate this equation in the same way as the original equation to get the equation: x≥3. This means that any value of x that is greater than or equal to 3