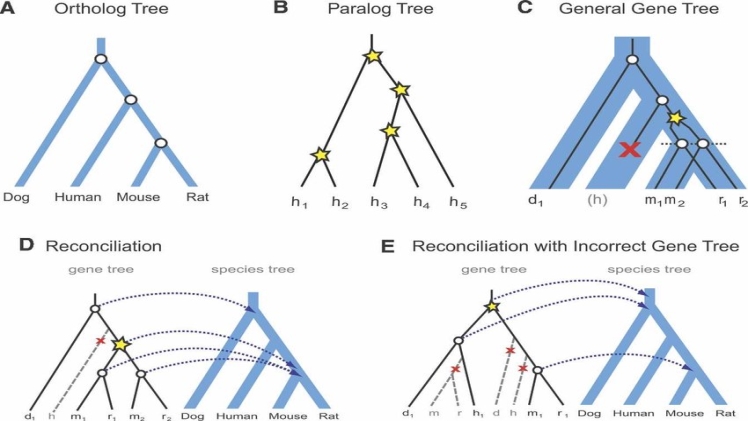
Genetics has long been an area of interest to biologists, as it provides insight into how organisms evolve and change over time. Orthologs, a type of gene found in many organisms, are a vital part of understanding these evolutionary relationships. This article will discuss the concept of ortholog assay and its use in understanding evolutionary relationships in genetics.
Orthologs are genes that have evolved from a common ancestor and share similar functions across species. An ortholog assay is used to compare the sequences of orthologous genes across species. By doing this comparison, biologists can gain insight into how genetic traits have changed throughout evolution and how they are related to each other.
By comparing the sequences of orthologous genes across species, scientists can investigate the underlying mechanisms of evolutionary processes such as natural selection and gene duplication. Additionally, this type of analysis provides insight into genetic diseases, which may be caused by changes in specific genes over time. In conclusion, ortholog assays provide an invaluable tool for exploring evolutionary relationships in genetics.
## 1. Definition Of Ortholog Assay
An ortholog assay is a tool used by researchers to study the evolutionary relationships between genes. It helps to identify homologous genes in various species and can provide insight into how these genes have changed over time. The assay involves the use of bioinformatics analysis, which is usually applied to DNA sequences from different species.
The goal of an ortholog assay is to compare genetic sequences from multiple species, allowing researchers to detect similarities and differences between them. This comparison can be used to infer how a gene has evolved over time. By utilizing this technique, scientists are able to better understand the underlying evolutionary processes that shape genetic diversity in nature.
In addition, ortholog assays can help researchers identify potential new therapeutic targets for diseases caused by genetic mutations or aberrant gene expression. Understanding the evolutionary relationships between genes can lead to the development of more effective treatments and improved outcomes for patients with genetic disorders.
## 2. Applications Of Ortholog Assay
Ortholog assay is a powerful tool for understanding evolutionary relationships in genetics. It allows scientists to compare and contrast the genes of different species to see which are most similar, and it has been applied in various contexts. This article will discuss some of the applications of ortholog assays.
One major application of ortholog assay is to assess gene function. By comparing closely related species’ genes, it can reveal which genes have evolved over time and thus show how they may have changed in function. This can be useful for studying diseases, as well as for working out how different species interact with one another. Additionally, ortholog assays can provide insight into the evolution of genetic traits across populations, which can help inform conservation measures.
Another application of ortholog assays is to identify potential drug targets. By studying the similarities and differences between two species’ genomes, scientists can more easily pinpoint regions that may be involved in disease pathways or other biological processes. This information can then be used to develop therapies that target those regions specifically, potentially leading to more effective treatments for a wide range of illnesses.
Ortholog assays are also valuable when it comes to understanding evolutionary relationships between organisms at both the macro- and micro- scales. By looking at how different species have evolved from one another over time, researchers can gain insight into how their characteristics have changed over time, allowing them to better understand the process of evolution itself.
## 3. Benefits Of Using Ortholog Assay
The use of ortholog assay to understand evolutionary relationships in genetics has a number of benefits. First, it can provide greater accuracy when determining the degree of relatedness between species. By measuring the homology between genes, scientists can compare the similarities and differences to gain insights into the evolutionary mechanisms that have shaped the genome structure and gene expression patterns over time. In addition, ortholog assay is beneficial for the development of genetic resources such as databases, which allow researchers to easily identify and access related genes from different species.
Another benefit is that it allows us to identify conserved regions in gene sequences which may be important for understanding functional differences between species. For example, by examining gene sequences from different species, researchers can note conserved regions that are likely involved in similar pathways or functions across multiple organisms. Furthermore, conserved regions can help identify potential disease-causing mutations in humans since they are shared with other species.
Ortholog assay also offers a cost-effective way to study evolution at the molecular level. This is because sequencing orthologous genes in different species requires much less effort than sequencing entire genomes or performing other types of evolutionary analyses. As such, it offers an efficient approach to studying large numbers of genomic data points and tracking changes in gene expression levels over time as well as within individual populations.
## 4. Analyzing Evolutionary Relationships In Genetics
The fourth step in understanding evolutionary relationships in genetics involves analyzing the data obtained from ortholog assays. This type of analysis can provide valuable insights into how organisms and species are related to each other. By analyzing the sequence homology and phylogenetic tree of the different species, researchers can gain an understanding of how genes have evolved and changed over time.
In addition, ortholog assays can also be used to study the impact of gene loss or duplication on evolution. By comparing different species, researchers can determine which gene has been lost or duplicated during evolution and investigate the effects that this has had on the organism’s phenotype. This type of analysis is important for understanding how organisms adapt to changes in their environment.
It is also possible to use ortholog assays to look for evidence of horizontal gene transfer between organisms. This process occurs when a gene from one organism is transferred directly into another organism, allowing it to gain new traits or capabilities not present in its ancestral lineages. By studying patterns of horizontal gene transfer, researchers can gain further insights into how organisms are related and what evolutionary forces are at work within a given population.
## 5. Interpretation Of Results From Ortholog Assay
Interpreting the results of an ortholog assay is essential in understanding evolutionary relationships in genetics. It involves examining the data to identify patterns and draw valid conclusions regarding the evolutionary history of a species. A key factor when interpreting the results is to consider whether there are any discrepancies between the observed data and what was expected from theory.
The interpretation of orthologous assays should include an assessment of the statistical significance of any detected patterns or trends. This requires appropriate tests, such as chi-square or Fisher’s exact test, which can determine whether particular similarities or differences between species are significant in terms of evolution. Further analysis may also be performed to assess if there are any conserved regions within a gene sequence that can indicate functional importance over time, i.e., if a gene has been conserved for several generations or experienced positive selection, this could suggest it is important for survival.
Once all relevant analysis has been conducted, findings should be presented in an understandable form, typically by creating tables and graphs to illustrate the data. This allows more accurate comparisons and enables researchers to draw more reliable conclusions about genetic relationships among species. Additionally, researchers can use these results as a basis for further experiments and research into evolutionary biology.
## Conclusion
The ortholog assay is a powerful tool for understanding evolutionary relationships in genetics. It provides insights into how two organisms have evolved over time, and the mechanisms that drive genetic divergence. Through this method, researchers can identify the genes that are most likely to be shared between two species and investigate their relatedness. Furthermore, it allows them to detect conserved gene regions, which can provide important clues as to how different species have adapted over time. The interpretation of results from the ortholog assay is also an important step in getting a comprehensive picture of evolutionary relationships between species.
The ortholog assay has many advantages over other methods for studying genetic relationships between species. It requires minimal sample preparation, making it faster and easier than other techniques such as PCR-based methods. Additionally, the assay can detect both direct and indirect orthologs with high accuracy. This allows for more detailed analysis of evolutionary relationships between different organisms on a genomic level. Finally, the results from an ortholog assay can be used to gain insight into functional aspects of gene divergence, such as gene expression patterns or protein-protein interactions.
Overall, the ortholog assay is a valuable tool for gaining insights into evolutionary relationships between species at a molecular level. It provides useful information about gene conservation and divergence across different organisms and can help researchers understand how various species adapt to changing environments over time. The technique is relatively quick and easy to perform compared to other methods, making it an attractive choice for researchers interested in studying genetic relationships between different organisms on an evolutionary scale.