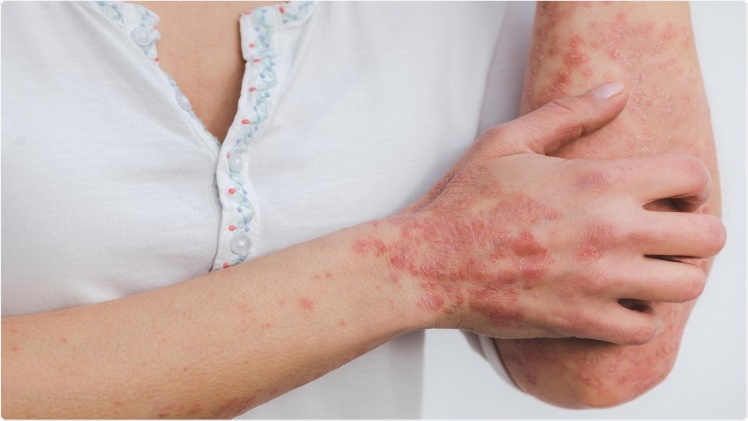
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, silvery scales and itchy, red patches. While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options are available to manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Causes and Triggers:
Psoriasis is believed to result from an overactive immune system that mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Genetics can play a role, as the condition often runs in families. Additionally, certain triggers can exacerbate psoriasis or lead to flare-ups, including stress, infections, injury to the skin, smoking, and certain medications.
Common Types of Psoriasis:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery scales. These patches can appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, and other areas.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, drop-like lesions that often appear on the torso, limbs, and scalp. It is often triggered by streptococcal infections.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, red lesions that develop in skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules surrounded by red skin. It can be localized to certain areas or cover the entire body.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe and rare form that leads to widespread redness and shedding of scales. It can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment Options:
Psoriasis treatment aims to reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell growth, and manage symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of psoriasis, as well as individual factors. Some common treatment approaches include:
Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Vitamin D analogs that help regulate skin cell growth.
- Topical retinoids to slow down cell turnover and reduce scaling.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
For more information regarding these treatments, visit a Best Skin Specialist in Karachi.
Systemic Medications:
- Oral or injected medications that target the immune system to reduce inflammation. These are used for more severe cases.
- Biologics: Injectable medications that specifically target parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis. They are often used for moderate to severe cases.
- Oral Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, these medications help control cell turnover and may be prescribed for severe psoriasis.
- Moisturizers and Emollients: Regular use of moisturizers can help soothe dry skin and alleviate discomfort.
Lifestyle Management:
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis:
- Maintaining a healthy weight and balanced diet.
- Avoiding triggers, such as stress and smoking.
- Practicing good skincare and hygiene.
- Using gentle soaps and avoiding harsh skin products.
Conclusion:
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition with various forms and triggers. While there is no cure, a range of treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Consultation with a Best Dermatologist in Lahore is imperative to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the type and severity of psoriasis.