A sports injury can change the life of an athlete, particularly if they rush to return to the field and take shortcuts as they recover from the injury. If not treated properly, sports injuries may result in years of reduced mobility, pain, and weakness that affect an athlete’s quality of life and ability to participate in their favorite sport. If pain is not managed properly, it can also result in more severe problems. A sports injury expert like Dr. Kevin McElroy can come up with a treatment personalized to the needs of an athlete, their injury, their level of pain, and their recovery.
Pain medication can be used for treating acute pain; however, non-pharmacological management measures must also be taken into account. These measures include the following:
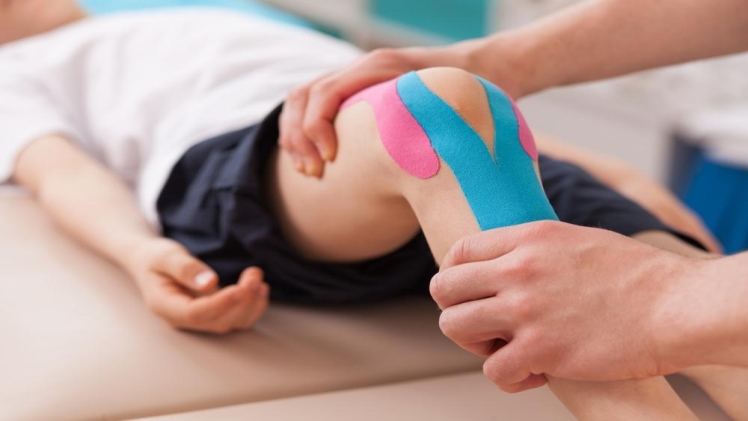
Physical Therapy
For most sports injuries, physical therapy is an effective treatment. A physical therapist identifies pain sources and offers therapy to increase strength, correct biomechanical problems, and build endurance. Although a lot of sports injuries may heal quickly without medical intervention, physical therapy helps correct the underlying issues that caused the injury to take place. These issues include poor biomechanics, muscle imbalance, and lack of flexibility. A therapist offers training suggestions and exercises to prevent another injury from happening.
Stretching and Strength Training
Strength training can help an injured athlete with their recovery. Conditioning and exercise can help with the production of anti-inflammatory effects and reduce pain feelings. Strength training and stretching are particularly important for young athletes who are going through significant growth spurts. Usually, the bones of these athletes grow too fast that their muscles and tendons may have difficulty adapting to it. This results in Sever’s disease and Osgood-Schlatter. A physical therapist can recommend controlled stretching to prevent such syndromes.
Psychosocial Interventions
As an athlete recovers from a sports injury, they may need to explore cognitive-behavioral therapies or psychosocial interventions. Psychological methods can begin right after injury to manage pain. Pain management is done through coping strategies and body control. These strategies also help identify the worries of an athlete and address such concerns.
Sleep
Sleep may reduce the risks of sports injury. However, pain disrupts sleep and a lack of quality of sleep increases pain. For athletes who have trouble sleeping during the recovery process, psychological strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapies and stress reduction may help.
Nutrition
Nutrition plays an important role in an injured athlete’s recovery process. But it’s important to remember that supplements won’t do the trick. Often, eating a balanced diet is key to getting the nutrients that an athlete needs.