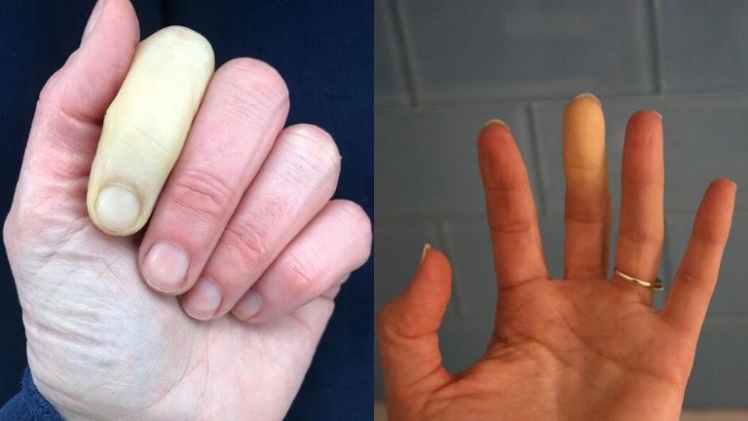
There are many health problems related to blood. Starting from hypotension, hypertension, anemia, to leukemia. In addition, there is also such a thing as Raynaud’s syndrome. This condition is caused by reduced blood flow to certain body parts. For example, on the fingers or toes, due to narrowing of the arteries. What is the impact of people with this syndrome on sufferers? Well, this condition will make your fingers or toes too sensitive in responding to cold temperatures. As a result, the skin will turn pale and turn blue. Keep in mind, there are times when this syndrome can also occur in the ears, nose, lips, and tongue. You can get aid in raynaud’s syndrome on our website.
Raynaud’s phenomenon occurs at all ages, but most patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon are women between the ages of 20 and 40 years.
Raynaud’s syndrome itself is divided into two types. First, primary Raynaud’s syndrome or Raynaud’s disease. This type most often occurs without any underlying medical condition. Fortunately, this condition can be mild and doesn’t need to be treated. Second, there is secondary Raynaud’s syndrome or Raynaud’s phenomenon. This one is caused by another medical condition. For example, autoimmune disease or arterial disorders. This type is more serious and definitely requires further treatment and examination in the hospital. As a result, blood circulation in the fingers or toes will be reduced.
1. Primary Syndrome
Women are more at risk for Raynaud’s phenomenon than men. In addition, Raynaud’s disease is also most common in the 15-30 year age group. People who have primary Raynaud’s, live in cold climates, and have a family history of the disease are also at increased risk of developing Raynaud’s phenomenon.
2. Secondary Syndrome
This syndrome is caused by factors, such as autoimmune diseases, arterial disorders, carpal tunnel syndrome, smoking habits, certain activities (such as typing or playing a musical instrument), certain drugs (beta-blockers), foot, or hand injuries, to exposure to chemicals. chemistry.
Symptoms of this syndrome begin in one finger or toe, but over time it will spread to other fingers. Well, here are the symptoms which are divided into three stages:
Stage 1. Cold temperatures will expose fingers or toes and make them turn pale due to reduced blood flow.
Stage 2. A lack of oxygen supply will make fingers or toes turn blue. The fingers will be cold and numb at this stage.
Stage 3. A normal blood flow will turn fingers or toes red again.
During this stage, the finger or toe will feel tingling, throbbing, and may experience swelling.
There are at least two complications that can be caused by Raynaud’s syndrome, such as:
Scleroderma. This condition is an autoimmune disorder that causes thickening or hardening of areas of the skin and connective tissue. This condition occurs because the body produces too much collagen.
Gangrene. Occurs when the arteries become completely blocked and cause infection. In rare cases, this gangrene can lead to amputation of the affected body part.
Certain factors that increase your risk of developing Raynaud’s phenomenon include:
a. Family history. Primary Raynaud’s can occur in members of the same family-related diseases. These include conditions such as scleroderma and lupus
b. Certain jobs. People whose jobs cause repetitive trauma, such as vibrating tools, may be more susceptible to secondary Raynaud’s
c. Smoking tobacco or using some medications such as:
– Beta-blockers are used for the treatment of high blood pressure
– Migraine, drugs containing ergotamine
– Medication for hyperactivity disorder or lack of focus
– Chemicals used for chemotherapy
– There are several cold and allergy medicines and diet aids on the market.
Having no risk factors doesn’t mean you can’t have Raynaud’s phenomenon. These factors are for reference only. You should consult your doctor for more details